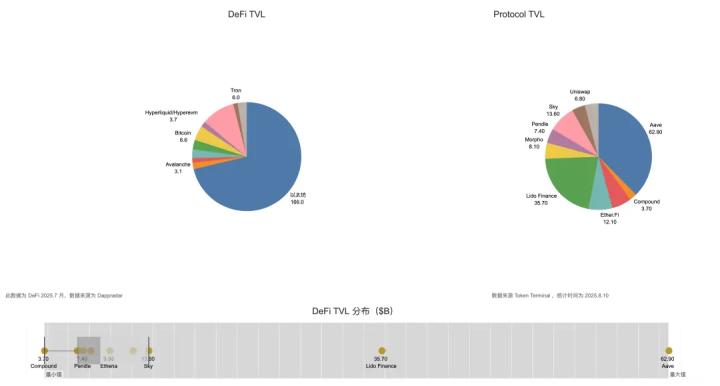
Large-scale long-term holding can reduce circulating supply, enhance recognition, and increase on-chain liquidity, but centralization, leverage, and operational risks mean that enterprise-level issues may be transmitted to the network.
Written by: Tanay Ved
Translated by: Saoirse, Foresight News
Key Points
- Digital asset reserves focused on Ethereum are rapidly expanding, accumulating 2.2 million ETH (1.8% of total supply) in just two months, causing a supply-demand imbalance.
- These treasuries are adopting proactive on-chain strategies, planning to allocate funds through staking and DeFi to increase returns while supporting network security and liquidity.
- Although currently in the accumulation phase, higher on-chain participation may enhance Ethereum's liquidity and security while increasing exposure to enterprise funding risks.
The Rise of Digital Asset Reserves
Digital Asset Treasuries (DATs), which are listed companies holding crypto assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum on their balance sheets, have become a new market entry channel. The launch of spot ETFs in 2024 has released demand from investors who previously could not hold BTC and ETH through direct custody. Similarly, digital asset reserves provide investors with an opportunity to access these assets and their ecosystems through publicly traded stocks, with the ability to strategically raise and allocate funds.
[The rest of the translation follows the same professional and accurate approach, maintaining the original meaning and technical nuances.]Linking Enterprise Treasury Performance with On-Chain Health Status
As the on-chain layout of listed Ethereum treasury companies continues to expand, their financial performance increasingly impacts the long-term network health of Ethereum, connecting off-chain corporate performance with potential on-chain influences. Large-scale long-term holdings can reduce circulating supply, enhance recognition, and increase on-chain liquidity, but centralization, leverage, and operational risks mean that enterprise-level issues may be transmitted to the network.
Impact of Large ETH Reserve Holdings on the Chain
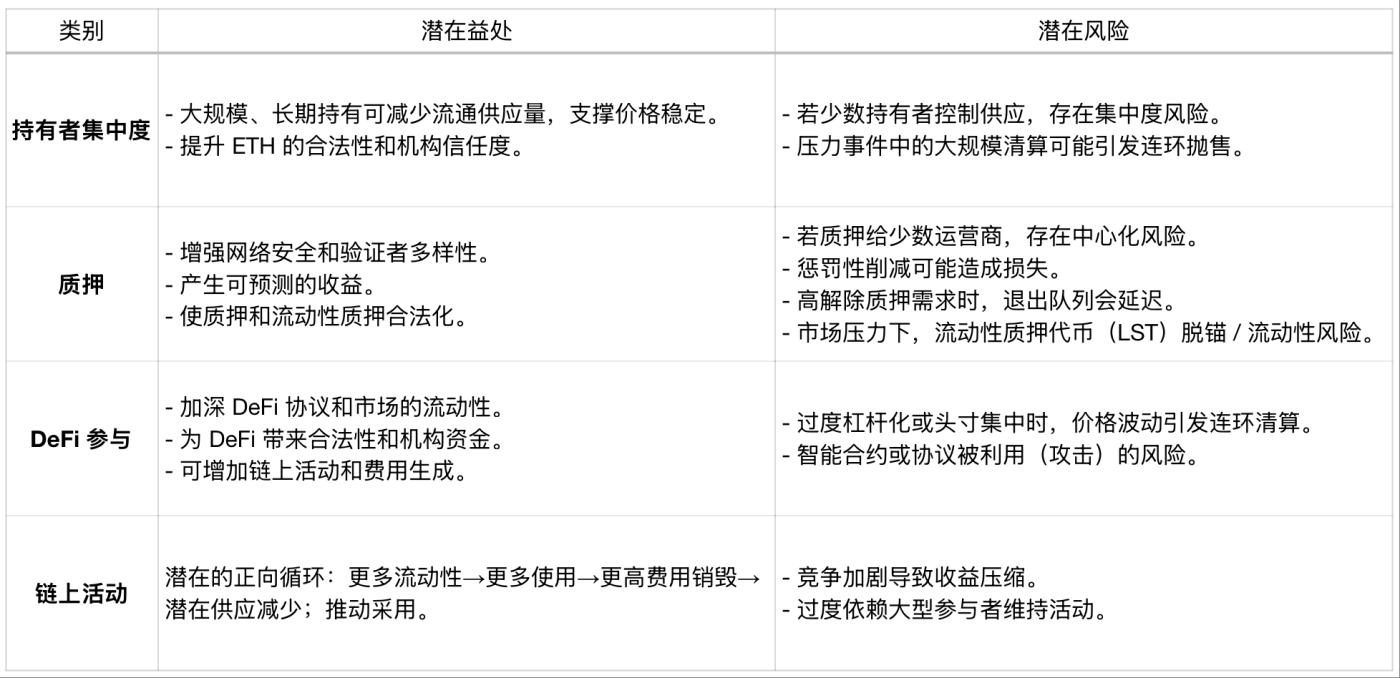
Although these are network-level considerations, treasury companies themselves are also influenced by market forces and investor sentiment. Strong balance sheets and continuous investor confidence can expand reserve holdings and increase participation. Conversely, significant drops in underlying asset prices, tightened liquidity, or over-leveraging could lead to ETH selling or reduced on-chain activity.
Indicators Related to Treasury Company Performance
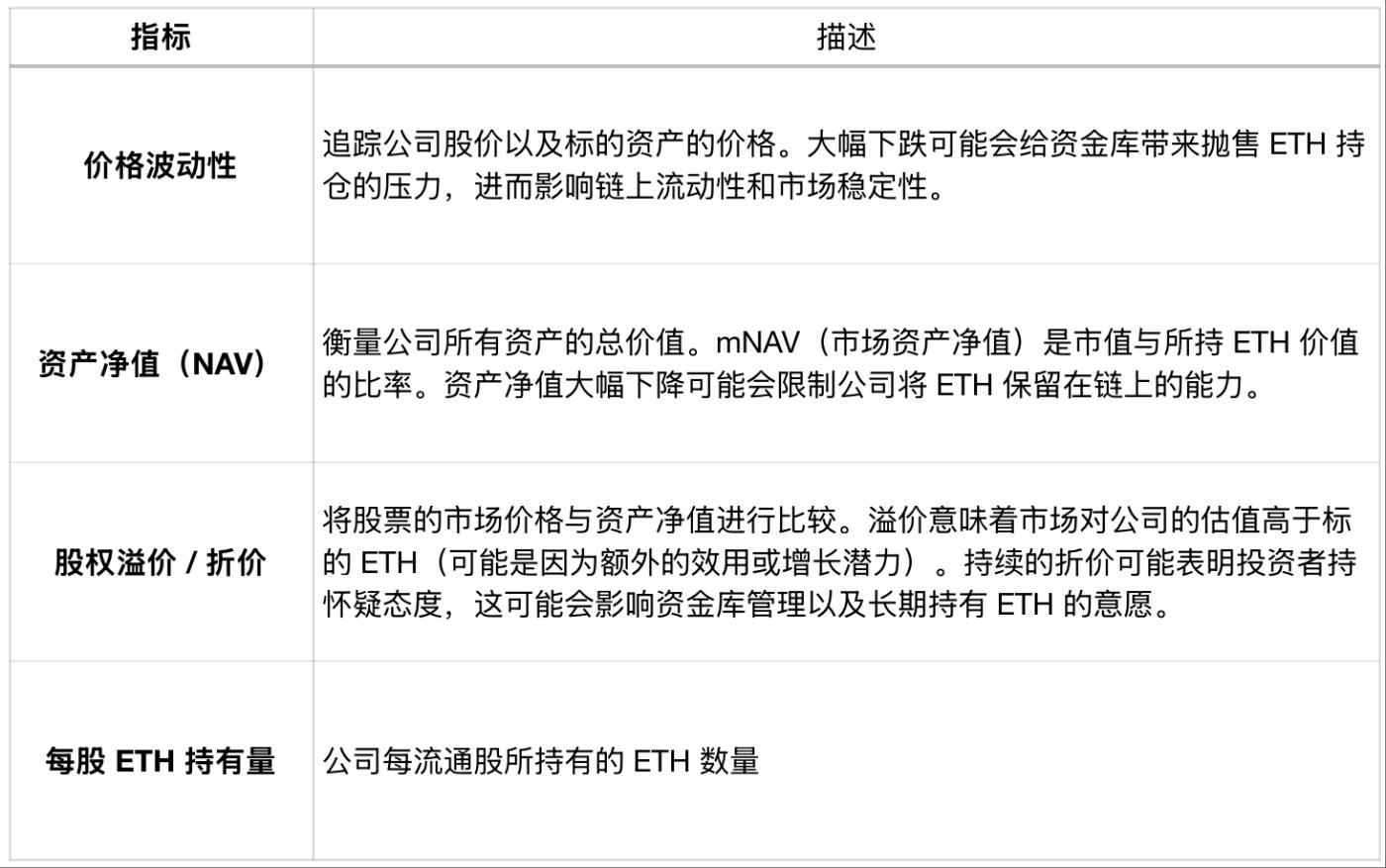
Indicators track price volatility of company stock prices and underlying assets. Significant drops may pressure treasuries to sell ETH holdings, thereby affecting on-chain liquidity and market stability. Net Asset Value (NAV) measures the total value of all company assets. mNAV (market Net Asset Value) is the ratio of market capitalization to held ETH value. A substantial NAV decline could limit the company's ability to retain ETH on-chain. Equity premium/discount compares the market price of stock to its NAV. A premium means the market values the company higher than the underlying ETH (possibly due to additional utility or growth potential). Persistent discounts might indicate investor skepticism, which could affect treasury management and willingness to hold ETH long-term. ETH per share is the amount of ETH held per outstanding share.
By tracking network-level impacts and the financial health of these companies, market participants can better predict how enterprise treasury behavior might influence Ethereum's supply dynamics and overall network health.
Conclusion
The rapid rise of enterprise Ethereum treasuries reflects Ethereum's attractiveness as a reserve asset and on-chain yield source. Their growing influence may increase liquidity and active network activity, but also comes with risks related to leverage, financing, and capital management. As off-chain factors like stock performance and debt repayment become more closely linked with on-chain activities, these factors could quickly impact on-chain dynamics. As these institutions expand, tracking their balance sheet health and on-chain activities will be key to understanding their impact.